TRL-4
Technology tested in the laboratory
Available laboratory prototype
Market and Economic Attractiveness
- High competitiveness and the need to replace hydraulic shock absorbers as pollutants of the natural environment in the face of growing environmental requirements.
- High specific dissipation energy of external mechanical action with subsequent possibility of damper miniaturization.
Main Advantages (Strengths) of the Device
- High specific energy intensity of the dissipation process (5-50 J/cm3);
- Max workload can exceed traditional analogues without loss of workability;
- Providing passenger comfort and increasing the life of the mechanical parts of the car by reducing and stabilizing efforts in response to mechanical disturbance from road obstacles;
- Ensuring reliable adhesion of the wheels to the road while maintaining maximum comfort for passengers;
- Constant force on the vehicle body in a wide range of speeds and frequencies of interference on the road.
Main Characteristics
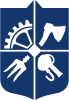
- Thermomolecular damper of automobile suspension with new heterogeneous working medium:
| Shock absorber operation amplitude | +/- 84 mm |
| Operating force on shock absorber | 1 kN |
| Shock absorber operating frequency range (compared to 4 ÷ 6 Hz for traditional hydraulic shock absorber) | 1-22 Hz |
| Required amount of heterogeneous working medium (instead of 1000 ÷ 1500 cm3 of technical oil) | 20 ÷ 25 cm3 |
Marketing Readiness
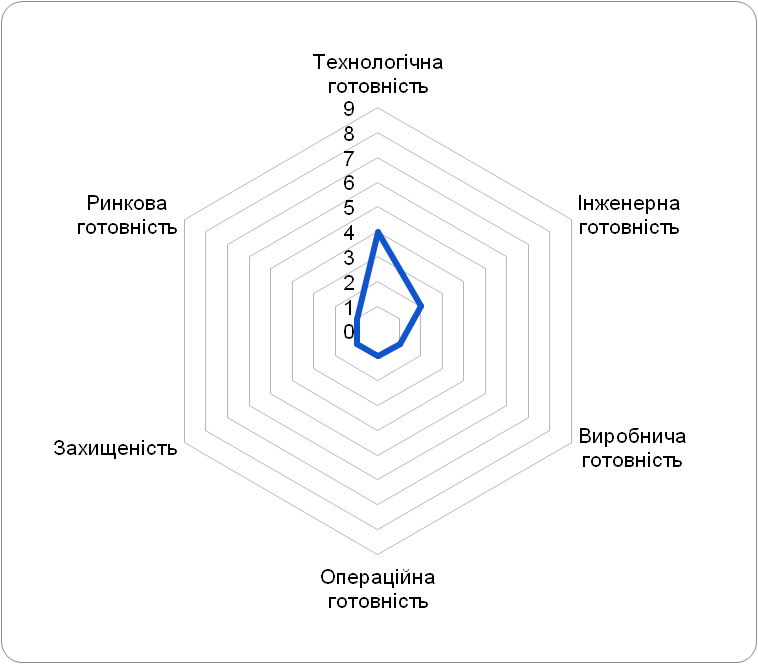

- Laboratory sample tested
- Analysis of the effect of the product on the entire system was carried out
- Basic production requirements are formulated
- Basic business process diagrams are defined
- Initial benefit and risk assessment completed
- Utility evaluation performed
Protection of intellectual property
- V.A Eroshenko, https://doi.org/10.1243/09544070D0150
- V.A Eroshenko, I.Piatiletov, L.Coiffard, and V Stoudenets, https://doi.org/10.1243/09544070D0160
Developer Information
- Research team NN IATE-18. Thermomolecular energy
What is Needed to Promote the Device
Financing for the development of pilot designs and their introduction into industrial production